28 min read
By: RedLegg's Cyber Threat Intelligence Team
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
RedLegg would like to recognize the efforts instituted by the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Agency (CISA), and the National Cybersecurity Alliance (NCA), in their ongoing mission to foster a security focused mindset across the digital community. Cybersecurity Awareness Month is collaborative call to action to raise awareness to the importance of digital security and"empowers others to protect their personal data from digital forms of crime".
RedLegg unites in the resolve to raise awareness and continue in the effort to safeguarding our digital realm, by delving into the world of Remote Monitoring & Management (RMM) tools – with a sinister twist. In this blog, we’ll unveil the eerie parallels we’ve uncovered between the supernatural board game depicted in the 2016 film, Ouija: Origin of Evil, and the use of RMM tools.
As we inch closer to the spookiest night of the year, we’ll be your guides as we embark on an RMM Seance to see how our threat landscapes also offers its own chilling tales. Join us as we summon cyber awareness and hack our way into this year’s #CybersecurityAwarenessMonth.
 Figure 1: Ouija Board Game
Figure 1: Ouija Board Game
 Board Game – Rule #1: Never Play Alone
Board Game – Rule #1: Never Play Alone
THE RMM SEANCE
The Ouija board in Ouija: Origin of Evil served as a channel for communication with the spirit world. Similarly, remote monitoring and management tools have a legitimate purpose and can act as a conduit for IT professionals to access and interact with distant systems and networks. Both involve the transmission of information across dimensions, although in vastly different contexts.
⚠️!SPOILER ALERT!⚠️
If you have not seen Ouija: Origin of Evil
there are spoilers in this blog.
⚠️!SPOILER ALERT!⚠️
Focusing on less astral planes, we’ll shift to a few RMM’s that have been observed in use by ransomware operators in reports as of late 2022 and well into 2023.
 Figure 2: Slingshot - "Legitimate" Use
Figure 2: Slingshot - "Legitimate" Use
AnyDesk
- Use associated with: Akira, AvosLocker, LockBit, BlackCat
Atera Agent
- Use associated with: AvosLocker, BlackCat, Hive, LockBit
ScreenConnect
SplashTop
- Use associated with: AvosLocker, BlackCat, Hive
TacticalRMM
- Use associated with: AvosLocker, BlackCat
You may recall familiar old ghost stories from years past about RMM abuse, like the one where REvil had decided to “mess with Texas” by utilizing stolen ScreenConnect credentials to login to compromised accounts lacking multi-factor authentication (MFA) via Tor exit nodes to deliver ransomware resulting in Texas declaring “the first cybersecurity incident to be deemed a state disaster” …or maybe you don’t!
 Figure 3: Slingshot - Adversarial Control
Figure 3: Slingshot - Adversarial Control
Whether you were previously familiar with how REvil leveraged ScreenConnect, we mention it because ScreenConnect was initially used legitimately and to provide remote support to users across various organizations. Due to a lack of additional identity and access management (IAM) controls like MFA being a requirement, the RMM was used against those who relied on it. While the remainder of our blog is not IAM focused, if you or one of your partners chooses to deploy an RMM within your organization, it is crucial to recognize how important the configuration choices related to RMM IAM may be for your organization. (If you need help with IAM, RedLegg has you covered.)
 Board Game – Rule #2: Never Play in a Graveyard
Board Game – Rule #2: Never Play in a Graveyard
MALEVOLENT ATTACK
As defenders, RMM tools are leveraged as operational support applications, that are used as solutions for automation, scalability, seamless management, and proactive monitoring for network security. RMM tools also help in streamlining day-to-day tasks such as software updates, system diagnostics, and patch management. However, they can also pose as an unsuspecting point of entry, or a vulnerable host in your environment if not properly maintained. Maintaining a comprehensive inventory of all software and thoroughly managing software updates helps to identify and/or eliminate any dead or “end-of-life” tools that may still be lurking in your environment.
While most RMM tools are developed and used for legitimate purposes, they offer tremendous power and versatility that can be harnessed constructively or for pure evil. RMM tools are equipped with sophisticated command and control features, that can be manipulated to infiltrate and takeover environments. Adversaries have been observed exploiting internal vulnerabilities (i.e. unpatched software, weak security policies) to gain unauthorized access, compromise system integrity, and exfiltrate sensitive data, effectively turning your organization's assets into "possessed" systems. The dual nature of RMM tools underscores the importance of robust security measures to protect against the potential misuse of these tools.

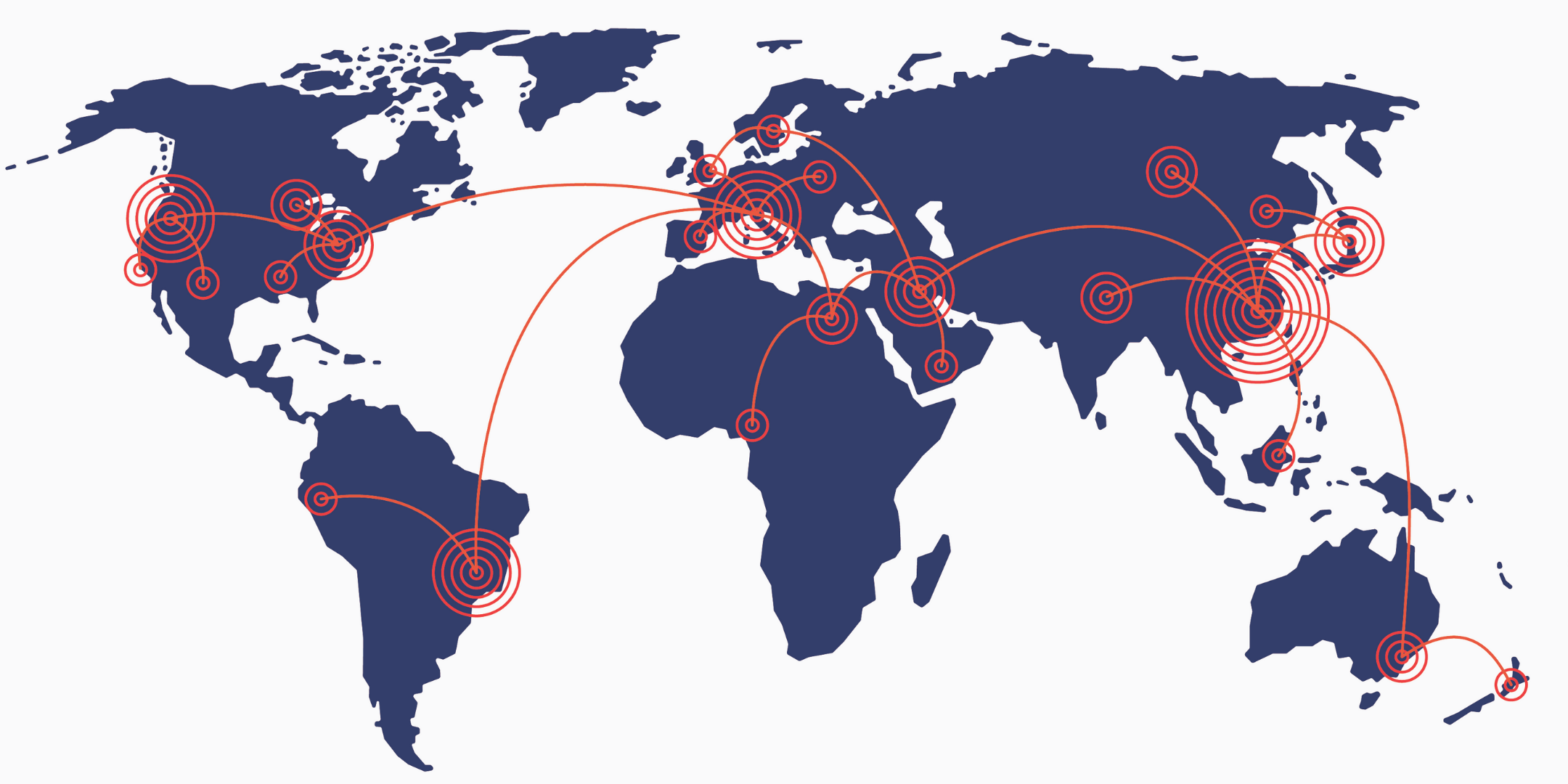
Figure 4: Adversarial Takeover (Command & Control)
Dual Ransomware
The FBI reported an increase in what they classify as "dual ransomware" on September 23rd 2023, declaring the occurrence of dual ransomware being observed when ransomware payloads are deployed twice or more within 10 days of an initial ransomware infection, and as short as 48 hours. Some of the ransomware affiliates that leverage the “dual ransomware” model that we focus on for exorcism in this post are AvosLocker and Lockbit. Both of these ransomware payloads are delivered by affiliates that leverage legitimate RMM utilities to “conjure up” the deployment of their ransomware payloads.
ALPHV (BlackCat) ransomware affiliate usage
Microsoft and Sophos have reported on ALPHV affiliates utilizing RMM’s prior to the deployment of BlackCat/Sphynx ransomware. Affiliates deploying BlackCat ransomware payloads utilized RMM tools such as AnyDesk, Atera, ScreenConnect, SplashTop, and TacticalRMM to maintain persistence and establish command and control within networks that were infiltrated.
MITRE ATT&CK TACTICS AND TECHNIQUES – Remote Monitoring & Management Tools
|
Initial Access |
||
|
Technique |
Identifier |
Notes |
|
External Remote Services |
||
Table 1: RMM ATT&CK Techniques for Initial Access
|
Command and Control |
||
|
Technique |
Identifier |
Notes |
|
Remote Services: Remote Desktop Protocol |
||
|
Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols |
||
|
Remote Access Software |
||
|
Protocol Tunneling |
||
Table 2: RMM Tool ATT&CK Techniques for Command and Control
 Board Game – Rule #3: Always Say Goodbye
Board Game – Rule #3: Always Say Goodbye
EXORCISING THE ADVERSARY
Here at RedLegg we write and deploy detection rule logic based on Sigma, "the generic signature format for SIEM", a vendor-agnostic detection rule writing language. We do this so that we can support detection capabilities for multiple platforms without being locked into any one vendor. If you are unfamiliar with Sigma, you can learn more at the Sigma website or by going directly to the Sigma project on GitHub. Sigma rules are built to follow the Sigma specification utilizing the YAML format .
Thankfully, even if you aren't leveraging the complimentary tools pySigma or Sigmac , YAML lends itself to being relatively human readable. If this is your first time attempting to read a Sigma rule, understanding field values can be confusing. Thankfully many of the below referenced field mappings are Sysmon based. TrustedSec maintains a Sysmon community guide that is a fantastic resource for understanding data field mappings in Sigma, such as those observed during process creation events. No matter how your organization is prepared to vanquish adversaries from your environment, understanding Sigma based rule logic can be invaluable. Consider joining the community and pushing up your own rules!
TRICK OR TREAT?
Much of this blog was focused on why you should identify RMM activity so we will leave you with some publicly available detection logic that can get you started with incorporating Sigma rules based on the RMM’s that we’ve focused on exorcising.
Identify RMM activity via process creation event logs:
AnyDesk
- proc_creation_win_remote_access_tools_anydesk.yml
- proc_creation_win_remote_access_tools_anydesk_susp_exec.yml
- proc_creation_win_remote_access_tools_anydesk_piped_password_via_cli.yml
- proc_creation_win_remote_access_tools_anydesk_silent_install.yml
- proc_creation_win_remote_access_tools_anydesk_susp_exec.yml
ScreenConnect
- proc_creation_win_remote_access_tools_screenconnect.yml
- proc_creation_win_remote_access_tools_screenconnect_remote_exec.yml
- proc_creation_win_remote_access_tools_screenconnect_anomaly.yml
- Note similarities: On occasion, newer detection rule logic has overlap with pre-existing detection rule logic. Depending on what you are attempting to detect, you may opt to integrate or exclude new logic and/or tune further internally.
- proc_creation_win_remote_access_tools_screenconnect_access.yml
Identify RMM activity via Windows Service Install and/or Security Extension event logs:
Service Install event log activity is not only great for identifying initial deployment of RMM utilities, just like the forces in Ouija could not refrain from making their presence known, services like Atera Agent have been known for their excessive telemetry utilizing Event ID 7045 in Windows Service Install event logs.
Atera Agent, SplashTop, and more
- win_security_service_install_remote_access_software.yml
- win_system_service_install_remote_access_software.yml
AnyDesk
TacticalRMM
Identify RMM activity via file event logs:
AnyDesk
ScreenConnect
- file_event_win_remote_access_tools_screenconnect_artefact.yml
- file_event_win_remote_access_tools_screenconnect_remote_file.yml
Identify RMM activity via DNS event logs:
AnyDesk, Atera, ScreenConnect, SplashTop, and more
If you are interested in finding more detection logic beyond what we have highlighted in our RMM blog, you can leverage the Sigma Search Engine or if what you are interested in is so "bleeding edge", you may want to monitor the pull requests for the project to stay current with any new developments for Sigma prior to their full publication. You may have also noticed that there are vacancies for detection logic for process creation events related to tools like Atera Agent, SplashTop, and Tactical RMM as well as many more detection opportunities that have not made their way into the community ruleset. Our Halloween themed list of RMM detection opportunities is not exhaustive and detection coverage in the open Sigma ruleset could be expanded. Thank you to all of those behind the Sigma project and contributors to the project past, present and future.
RMM tools can either safeguard our digital dominion or become conduits for malevolent forces haunting your network. Take control of your domain and let’s work to #SecureOurWorld!
REFERENCES
Bank Info Security. (2022, February 22). The Ransomware Files, Episode 5: Texas and Revil.
https://www.bankinfosecurity.com/interviews/ransomware-files-episode-5-texas-revil-i-5028
CISA. (2023, June 14) aa23-165_understanding_TA_LockB.
https://www.cisa.gov/sites/default/files/2023-06/aa23-165a_understanding_TA_LockBit_0.pdf
CISA. (2023, October 11). aa23-284a-joint-csa-stopransomware-avoslocker.
https://www.cisa.gov/sites/default/files/2023-10/aa23-284a-joint-csa-stopransomware-avoslocker-ransomware-update.pdf
CISA. (2023, October). Cybersecurity Awareness Month.
https://www.cisa.gov/cybersecurity-awareness-month
CISA. (2023). 2023 Cybersecurity Awareness Month Partner Toolkit.
https://www.cisa.gov/sites/default/files/2023-09/Cybersecurity%20Awareness%20Month%202023%20Toolkit%20Guide%20FINAL_508c.pdf
CISA. (n.d.). Cybersecurity Awareness Month 2023 Resources and Partner Toolkit.
https://www.cisa.gov/resources-tools/resources/cybersecurity-awareness-month-2023-resources-and-partner-toolkit
CISA. (n.d.). Secure Our World Tip Sheets.
https://www.cisa.gov/resources-tools/resources/secure-our-world-tip-sheets
FBI. (2023, September 27). PIN | 230928.
https://www.ic3.gov/Media/News/2023/230928.pdf
Infosec Exchange. (2023, September 13). Sophos X-Ops: “During the intrusion, the threat…”.
https://infosec.exchange/@SophosXOps/111059622083722634
Microsoft. (2023, October 25). Octo Tempest crosses boundaries to facilitate extortion, encryption, and destruction.
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/security/blog/2023/10/25/octo-tempest-crosses-boundaries-to-facilitate-extortion-encryption-and-destruction/
Microsoft. (n.d.). What is Identify Access Management (IAM)? | Microsoft Security.
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/security/business/security-101/what-is-identity-access-management-iam
MITRE | ATT&CK. (n.d.) Matrix – Enterprise.
https://attack.mitre.org/matrices/enterprise/
National Cybersecurity Alliance. (2023, October 1). Cybersecurity Awareness Month.
https://staysafeonline.org/programs/cybersecurity-awareness-month/
Sophos News. (2023, May 9). Akira Ransomware is “bringin’ 1988 back”.
https://news.sophos.com/en-us/2023/05/09/akira-ransomware-is-bringin-88-back/
Texas Department of Information Resources. (2021, November 8). US Justice Department Announces Indictment Against REvil Ransomware Suspect Behind 2019 Ransomware Attack on Texas Municipalities.
https://dir.texas.gov/news/us-justice-department-announces-indictment-against-revil-ransomware-suspect-behind-2019
The DFIR Report. (2023, September 25). From ScreenConnect to Hive Ransomware in 61 hours.
https://thedfirreport.com/2023/09/25/from-screenconnect-to-hive-ransomware-in-61-hours/
Universal Pictures Home Entertainment. (n.d.). Ouija: Origin of Evil.
https://www.uphe.com/movies/ouija-origin-of-evil
Wikipedia. (2023). Tor (network).
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tor_(network)
What’s lurking
in your
environment?
 Figure 5: Who's Watching Your Network?
Figure 5: Who's Watching Your Network?